As more and more laptops with the latest 12th Gen Intel and AMD Ryzen 6000-series processors come out, it seems like Intel is finally reclaiming the lost positions of the last two years from AMD. The new big.LITTLE design with separate cores for performance and efficiency-based tasks really did the trick for Intel, at least in terms of performance. While AMD also not giving Intel an easy win, the laptops with the latest Ryzen 6000 series processors are on the whole another level when it comes to efficiency.
The battle is undoubtedly very strife this year, and it’s indeed not easy to select between AMD or Intel for laptops this year.
To help you with it, we have put together this in-depth guide where we’ve compared the latest AMD Ryzen 6000 series processors with the 12th Gen Intel processors for laptops so that you can decide whether it is Intel or AMD laptop the right pick for your needs.
But before we start with the comparison, it’s important to know what’s new in AMD’s Ryzen 6000 series and Intel’s 12th Gen processors for laptops in comparison to their predecessors.
It will help you understand whether the laptops with the new-gen CPUs from Intel and AMD are really worth buying or if you’ll be okay buying last year’s laptops at discounted prices.
What’s New in Intel 12th Gen and AMD Ryzen 6000 Series Laptop CPUs?
The biggest draw of the Intel 12th Gen CPUs is its new hybrid architecture—featuring a separate set of P and E cores with different base and turbo clock frequencies. The CPU smartly splits the load between them depending upon the task at hand to deliver the best performance when needed with P-cores and only utilizing the E-cores when you are doing basic tasks to conserve the battery power.
On the other hand, AMD Ryzen 6000 series, unlike Intel 12th Gen, is more or less an improvement to the already great 5000 series mobile CPUs from last year. AMD has further optimized its Zen 3 core architecture used in 5000 series mobile CPUs to deliver even better performance per watt. Hence, AMD’s Ryzen 6000 series core architecture is called Zen 3+.
Also, it’s worth noting that AMD has switched to a 6nm process with the 6000 series AMD CPUs, whereas 12th Gen Intel processors still use the 10nm process!
If you don’t know what that means, think of it as AMD’s latest 6000 series CPUs are using smaller 6-nanometer parts inside the CPU, whereas Intel has larger 10-nanometer parts. The smaller parts are better as they allow more parts to fit inside the CPU, leading to better performance. And smaller parts also consume less power than larger parts, and less power equals less heat.
So, AMD’s Ryzen 6000 series powered laptops will run cooler and have longer battery life than the Intel 12th Gen powered laptops. Still, the raw compute performance of the 12th Gen Intel processors will be better than Ryzen 6000 series CPUs because Intel CPUs have more physical cores than AMD (more on that later).
Besides great efficiency, AMD added one more feather in the cap this year with 6000 series laptop CPUs, which is integrated graphics based on the latest RDNA 2 architecture. It’s the same GPU architecture used by AMD for Xbox Series X/S and Playstation 5! (Yes, Xbox and Playstation use AMD hardware!)
AMD claims their new RDNA 2-based integrated Radeon graphics is about 300% more powerful than Intel’s integrated Iris Xe graphics and outperforms even Nvidia’s entry-level MX series dedicated GPUs!
We will confirm that in a bit, but if accurate, such a level of iGPU performance will enable people to enjoy AAA games even on thin and light productivity-focused laptops!
Other Features of AMD Ryzen 6000-series and 12th Gen Intel Core Mobile CPUs
| Features | 12th Gen Intel Core Mobile Processors | AMD Ryzen 6000 series Mobile Processors |
|---|---|---|
| Codename | Alder Lake | Rembrandt |
| Core Architecture | Hybrid Architecture: All new architecture with separate performance and efficiency cores. | Zen 3+: More optimized version of already great Zen 3 cores of last year. |
| Process Node | Intel7 (10nm) | 6nm |
| Integrated Graphics | Intel Iris Xe for 12th Gen processors | AMD Radeon RDNA 2 based |
| RAM Support | DDR5 & DDR4 | DDR5 |
| PCIe Support | Gen 4 | Gen 4 |
| Connectivity | Thunderbolt 4, Wi-Fi 6E | USB 4, Wi-Fi 6E |
So, all in all, AMD’s Ryzen 6000 series CPUs are only marginally more powerful than the outgoing Ryzen 5000 series laptop CPUs. In contrast, the 12th Gen Intel CPUs bring considerable improvement compared to outgoing 11th Gen Intel CPUs.
Still, the AMD Ryzen 6000 series is able to give tough competition to the vastly improved 12th Gen Intel CPUs! That gives us an idea of how far behind the last year’s 11th Gen Intel processors were in comparison to AMD’s Ryzen 5000 series laptop CPUs.
So, the conclusion that comes out from all that we have discussed up until now is:
If you are on a budget and looking for a good value deal, you can consider the last year’s laptop with AMD Ryzen 5000 series processor if it’s available for a significant discount, but avoid buying last year’s 11th Gen Intel laptops because they are no more good value at this point.
Now that you know everything about all the new things that the latest Intel and AMD processors have to offer for laptops this year. Let’s start with a detailed comparison between them to determine, which processor laptop, Intel or AMD, will be right for you to buy in 2022.
AMD Ryzen 6000 Series vs. Intel 12th Gen Mobile CPUs – Detailed Comparison
So, let’s start by discussing how we will compare these CPUs so that you can better understand the comparison charts below and come to your own conclusion based on your computing needs. And to do that, it is important to understand (or, if you already know, recap) the different types of Intel and AMD CPUs available for laptops.
As we all know, different types of Intel processors are Core i3, i5, i7, and i9, and for AMD, it’s Ryzen 3, 5, 7, and 9. These numbers state the performance tier of different Intel and AMD CPUs where Core i3 and Ryzen 3 are the least powerful, and Core i9 and Ryzen 9 are the most powerful.
However, you might not know that all these CPUs are also further categorized into different types called U-series, P-series, and H-series processors. These alphabets in the name of processor state the nature of that processor (performance-focused or efficiency-focused) and the type of laptop they are suitable to fit in.
For instance, U-series processors (ultra-low power CPUs) are meant for thin and light laptops that focus more on battery life than performance, whereas H-series processors (high-performance processors) are for gaming laptops and content creation notebooks that focus more on performance than conserving power. Intel and AMD both have U and H-series processors in their lineup, but P-series processors are only available in Intel.
The P-series processors are relatively new and were introduced this year with the launch of the 12th Gen mobile CPUs by Intel. They power thin and light performance laptops that offer a balance of both performance and battery life.
How to identify if the processor is U, P, or H-series?
To identify if the processor is U, P, or H-series, check the name of the CPU. If the CPU’s name has the ‘U’ alphabet at the end, it is a U series processor. Likewise, if it has ‘P’ or ‘H’ in the end, it is P-series and H-series processor, respectively.
Example:
- AMD Ryzen 7 6800U and Intel Core i7-1255U are U-series processors.
- AMD Ryzen 7 6800H and Intel Core i7-12700H are H-series processors.
So depending upon your performance requirements and the type of laptop you want to buy, you can select the right CPU series for your needs.
If you want to buy a thin and light laptop with full-day battery life and good enough performance for everyday jobs, look for laptops powered by U or P-series processors. If you want to buy a high-performance laptop for gaming, photo/video editing, CAD, animation, or any other intensive workload, then laptops with H-series processors are the ones you should consider.
Now that you know about all the latest CPUs and their types let’s start with the comparison.
First, we will compare AMD Ryzen 6000 U-series processors with Intel’s 12th Gen U and P-series processors, and then after that, we will compare the H-series processors from both.
Intel 12th Gen U & P-series vs. AMD Ryzen 6000 U-series Processors
So let’s start by comparing the Geekbench 5 scores of different Core i3, i5 and i7 12th Gen Intel U and P-series processors to see how they stack up in comparison to AMD Ryzen 3, 5, and 7 6000 U-series processors.
For those who don’t know, the Geekbench benchmark gives us two scores, a single-core score and a multi-core score which gives us an idea of how well a CPU can perform in different single-core and multi-core workloads.
With that in mind, have a look at the scores below.
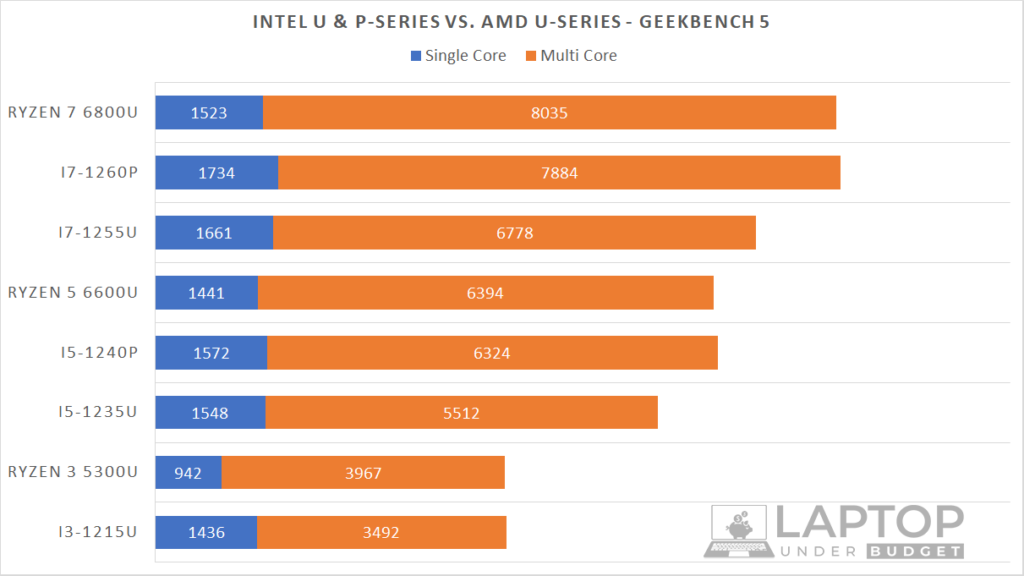
As you can see in single-core tests, in almost every comparison, Intel is leading here, but it’s not beating AMD by a huge margin. There’s hardly a difference of 100 points between them which does not make a lot of difference in performance.
But, if you check the multi-core scores, in almost every comparison, U-series AMD processors outperform Intel’s 12th Gen U-series processors by a noticeable margin and are neck on neck with Intel’s P-series laptop CPUs.
So, while AMD’s U-series processors are much better in comparison to Intel’s U-series processors in multi-core workloads, Intel’s P-series processors can still give tough competition to AMD’s U-series processors.
So, is it a tie?
Well, not until we bring the TDP of these CPUs into comparison.
Wait, what the heck is the TDP of the CPU now?
TDP (Thermal Design Power) is the amount of power (in watts) a CPU consumes.
Now that we have performance numbers of these CPUs seeing how much power they consume to put out this performance will give us an idea about their efficiency.
| Processor | TDP |
|---|---|
| 12th Gen Intel U-series | 15-55W |
| 12th Gen Intel P-series | 28-64W |
| AMD Ryzen 6000 U-series | 15-28W |
So, did you notice the trend here? Intel’s U and P-series processors are consuming a lot more power than AMD’s U-series, still AMD is able to keep up, if not fully able to outperform Intel!
What this means is, the laptops powered by the latest AMD Ryzen 6000 U-series processors will have much longer battery life than 12th Gen Intel powered laptops because they consume less power, and low power consumption also means less heat, meaning a cooler running laptop.
We all appreciate that, right?
We don’t want to keep looking for power outlets when we are out with our laptops or get irritated by the noise of fans whirring at full speed when we are trying to focus.
However, before we decide the winner of this comparison, there’s one more thing we need to compare these CPUs at, and that is their integrated graphics.
Since the U-series processor-powered laptops do not generally come with dedicated GPUs, they rely heavily on integrated graphics for gaming and other graphics-related tasks.
So, it’s important to know whether the integrated graphics performance of 12th Gen Intel processors is better or if it’s the AMD Ryzen 6000 series processors who’ll take the crown here as well. Let’s find out.
12th Gen Intel Iris Xe vs. 6000-series AMD Radeon RDNA 2 Integrated Graphics
To do this test, we will compare the 3DMark Time Spy score of integrated graphics of these processors. Not delving much into the details of that. Just keep in mind that the score here is the indicator of how better the iGPUs on these processors can handle gaming.
With that in mind, let’s have a look at the scores now.
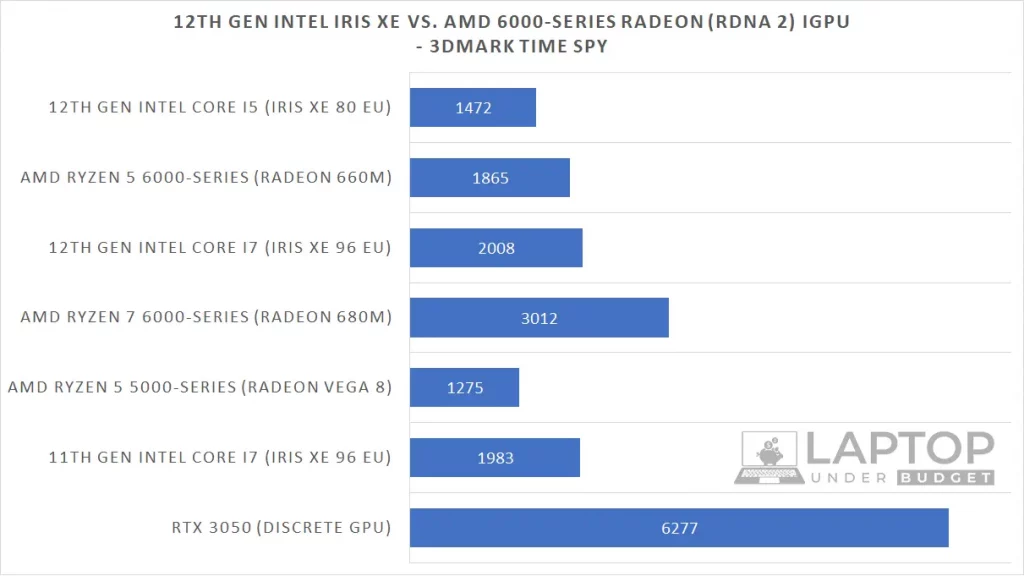
As you can see, again, AMD has emerged as a winner in this test with its RDNA 2-based Radeon 660M and 680M graphics outperforming Intel’s Iris Xe graphics by a pretty significant margin.
With the 3DMark Time Spy score of 3012, AMD Ryzen 6000 U-series CPU-powered laptops will be able to run almost every latest game at low settings using its iGPU. And older and less demanding titles like CS:GO, Valorant and Fortnite will easily reach above 60 FPS even in medium settings!
Also, to give you an idea, we have also included the integrated graphics scores of last year’s 11th Gen Intel and 5000 series AMD laptop CPUs so that you can know how better is the iGPU performance of the latest CPUs, and there’s also a score for dedicated Nvidia RTX 3050 based laptop for comparison.
So, undoubtedly AMD is the winner of this U & P-series comparison of the latest 12th Gen Intel and AMD Ryzen 6000 CPUs that power thin and light everyday use laptops.
But does this trend remain the same with the H-series processors as well?
Let’s find out.
AMD Ryzen 6000 H-series vs. 12th Gen Intel Core H-series Processors
Below is the Geekbench 5 score comparison chart of Intel Core i5, i7 and i9 12th Gen H-series processors and AMD Ryzen 5, 7 and 9 6000 H-series CPUs.
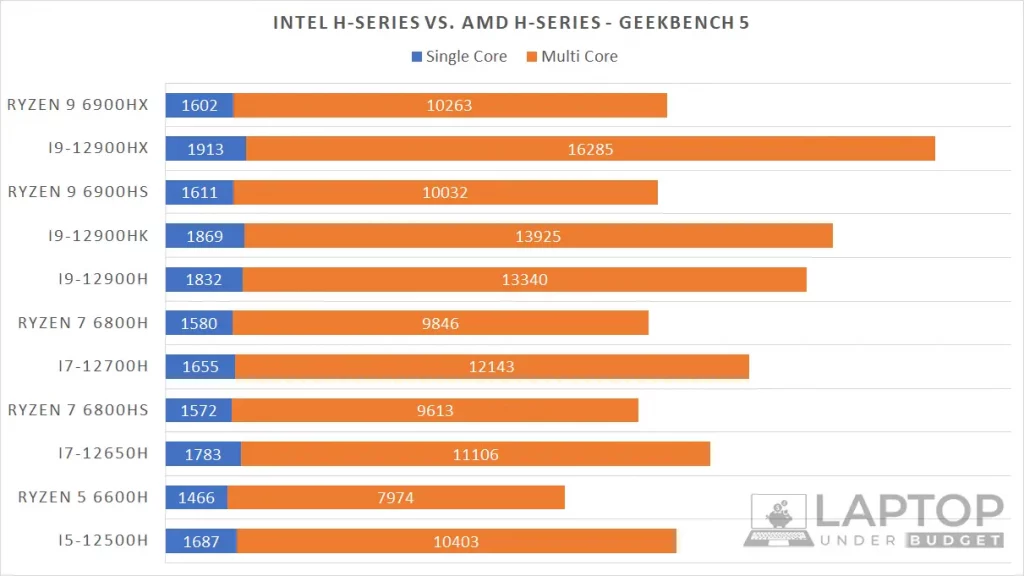
As you can see, the result is completely flipped now, with Intel leading in both single-core and multi-core tests for every comparison. That’s because Intel 12th Gen H-series CPUs have almost double the cores than AMD Ryzen 6000 H-series processors. For instance, the Core i9-12900HX has a total of 16-cores (8 Performance and 8 Efficiency), whereas its direct competitor Ryzen 9 6900HX still tops at 8-cores.
So with almost 60% better performance than AMD in a few cases, Intel 12th Gen H-series processor-powered laptops are going to be a better choice for power users.
Before we come to the final conclusion, though, let’s also have a look at the TDP difference of these Intel and AMD H-series processors.
| Processor | TDP |
|---|---|
| 12th Gen Intel H-series | 45-115W |
| AMD Ryzen 6000 H-series | 45W |
| AMD Ryzen 6000 HS | 35W |
| 12th Gen Intel HX | 55-157W |
| AMD Ryzen 6000 HX | 45W |
So, again as you can see, the power consumption of AMD processors is much lower than their Intel counterparts.
Of course, extra power draw is resulting in better performance for Intel, but expect Intel laptops to have much worse battery life than AMD laptops. Also, Intel laptops will need more powerful cooling systems (aka louder fans) to cool them effectively.
Still, Intel is outperforming AMD by a pretty large margin here, so it is undoubtedly Intel who won this comparison.
But, it’s AMD who is offering a well-rounded CPU here. For many people, it’s not just about the best performance. They also want good battery life so they can use their laptop like a “laptop”, from different places and without the charger plugged in all the time. And for many people like musicians and singers, a laptop’s fan noise can hinder when recording, so a laptop that stays cool and quiet under stress is essential for them.
So, ultimately it comes down to your own personal needs.
If you are someone who wants the most power in your laptop and battery life and fan noise does not matter much to you, the 12th Gen Intel H-series processor-powered laptop is the one you should get.
However, if you are a person who is okay buying a laptop that’s not the most powerful available for the price but can run all the latest games and professional applications just as good as them and also offers a great battery life, and stays cool and silent most of the time, then AMD Ryzen H-series laptops are the one for you.
Conclusion
While Intel has certainly made a comeback with its 12th Gen Intel CPU for laptops, it still can’t touch AMD at its efficiency. The excellent efficiency and RDNA 2-based integrated graphics make AMD a no-brainer choice in the thin and light laptops segment.
But Intel’s H-series 12th Gen CPUs are outright the best option if you are a power user with almost desktop-level performance on a laptop. Still, for those who need good battery life on their laptop along with great performance, AMD Ryzen 6000 H-series laptops will be a better option.
So, we hope that based on the comparisons we made here, you were able to decide whether it’s Intel or AMD the right laptop for you.
Found this article helpful? Tell us by making a thank you comment below (we love reading them).
Think we missed out on an essential point for this comparison to discuss in the article? Let us know of that as well in the comments below. Let’s help each other pick the right processor laptops for our needs.
Read Next:
- Top 10 Best Intel Core i9 Laptops
- Top 10 Best Intel Core i7 Laptops
- The Best Intel Core i5 Laptops Right Now
- Top 10 Best Intel Core i3 Laptops
- The Best AMD Ryzen Laptops Right Now




